The skin is unique in that it’s not only the largest organ of the body but also the most exposed. This vulnerability leaves the skin in a condition of high risk for contracting a disease, developing an infection, suffering infestation, and being in direct exposure to harmful environments such as extreme heat.
Skin infections are widespread and are seen regularly in all medical practices. The good news is that while there’s certainly a spectrum of severity when it comes to skin infections, most are relatively easy to treat, and they are easy to avoid when using proper hygiene.
Skin infections are still prevalent and must be treated diligently.
What follows is information on the types of skin infections and examples of each and how to treat and prevent them.
What is a Skin Infection?
Skin infections are a reaction to bacteria invading the skin and subcutaneous tissue beneath it. If your skin is red, swollen, and sore, you may have a skin infection of some sort.
Skin infections have a wide spectrum of signs and symptoms, side effects, severity, and types. Mild cases may simply require at-home remedies or over-the-counter antibiotic ointment, while more serious infections may require immediate medical attention and potentially IV antibiotics.
Types of Skin Infections
The four main categories of skin infections are: bacterial, viral, parasitic, and fungal. Each category is defined by its cause. Each category of infection contains numerous types of infections, and what follows is those details.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are caused by bacteria intruding on the skin and into the deep tissue, causing various effects and symptoms. Here are some of the most common examples of bacterial infections:
Impetigo: This conspicuous bacterial skin infection is most commonly present in young children. Impetigo causes red sores and blisters around the face but can also be found around the neck, hands, and groin region.
Impetigo can usually be cleared up in time with some basic topical antibiotics such as Bactroban. On occasion, the infection may not improve or can become worse, which will then require treatment with oral or IV antibiotics.
Though irritating, impetigo doesn’t tend to persist if taken care of properly.
MRSA: Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus, MRSA, is a more serious bacterial infection that medical treatment doesn’t always resolve. MRSA is common bacteria found in infections and abscesses that develop in the skin.
This type of bacteria can be quite resistant to usual antibiotics used for other skin bacteria. Some of the people most at risk of getting this type of infection are athletes, medical professionals, and childcare workers.
Skin Abscess: A skin abscess is a walled-off collection of fluid or pus that develops in the skin. Often these will require incision and drainage to remove the material in the abscess and allow healing. On occasion, they can heal without incision and drainage, but it depends on the size of the abscess.
Skin abscesses that don’t receive treatment and get larger can spread to surrounding areas and cause a much larger infection that can be very dangerous. It’s best to treat these conditions early to prevent this scenario.
Cellulitis: This is a severe skin infection that results in extreme redness, hotness, and tenderness of the skin. Often seen on the lower leg, cellulitis can be found throughout the body.
If the infection travels into the deeper layers of the skin, cellulitis can become a medical emergency that requires hospitalization.
Viral Skin Infections
Examples of viral infections of the skin are:
• Chickenpox
• Shingles
• Warts
• Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Parasitic Skin Infections
Examples of parasitic skin infections are:
• Hookworm
• Cutaneous Larva Migrans
• Lice
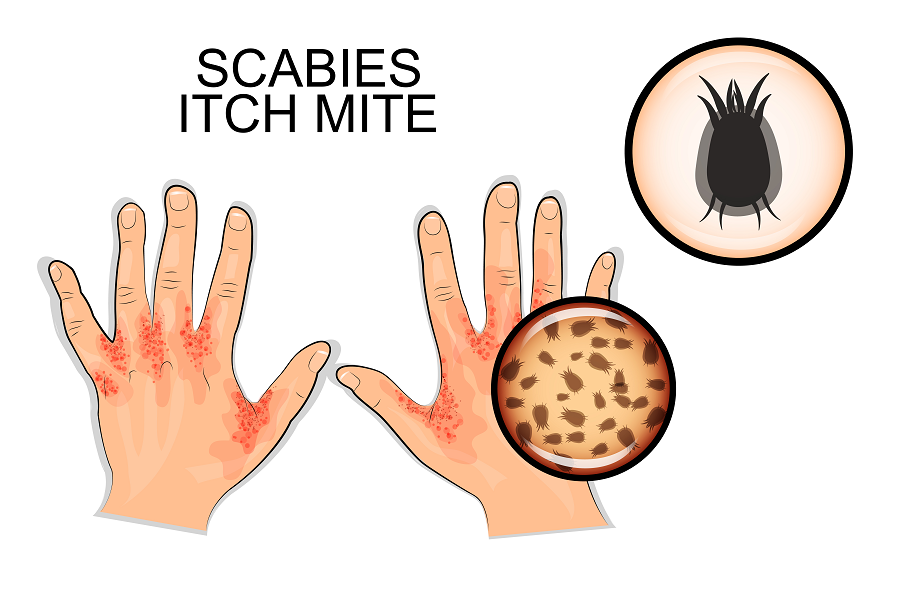
• Scabies
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are caused by fungus that is found in and around areas of the body, most typically areas that are less exposed, like the feet or axilla. Some of the more common examples of fungal infections are:
• Ringworm
• Nail Fungus
• Yeast Infection
• Athlete’s Foot
Skin Infection Treatments And Prevention
If skin infections are not treated promptly, they can become much worse and lead to bad outcomes.
In contrast, when treated early, skin infections tend not to be a major medical concern. Nonetheless, when diagnosed expeditiously, treatment is extremely effective.
If you come down with a more severe bacterial infection, however, topical ointments and antibiotics will likely be the primary prescription.
In other more severe cases, stronger antibiotics and treatment such as surgery may be required.
For fungal infections, a simple over-the-counter spray or cream will usually suffice.
The best prevention of skin infections is achieved through good hygiene and avoidance of unclean environments.
Final Thoughts
If you’re like the majority, you likely only need time and some simple at-home remedies to cure a skin infection. If infections of the skin are more severe, they can be managed by oral or IV antibiotics. Prevention of many of these skin infections can often be achieved by good hygiene.
If you have any concerns at all, regarding a skin infection, make sure you promptly seek medical help.